Lubricants in animal feed preparation
Recommended lubricants in animal feed preparation. Products of Fuchs Lubricants.
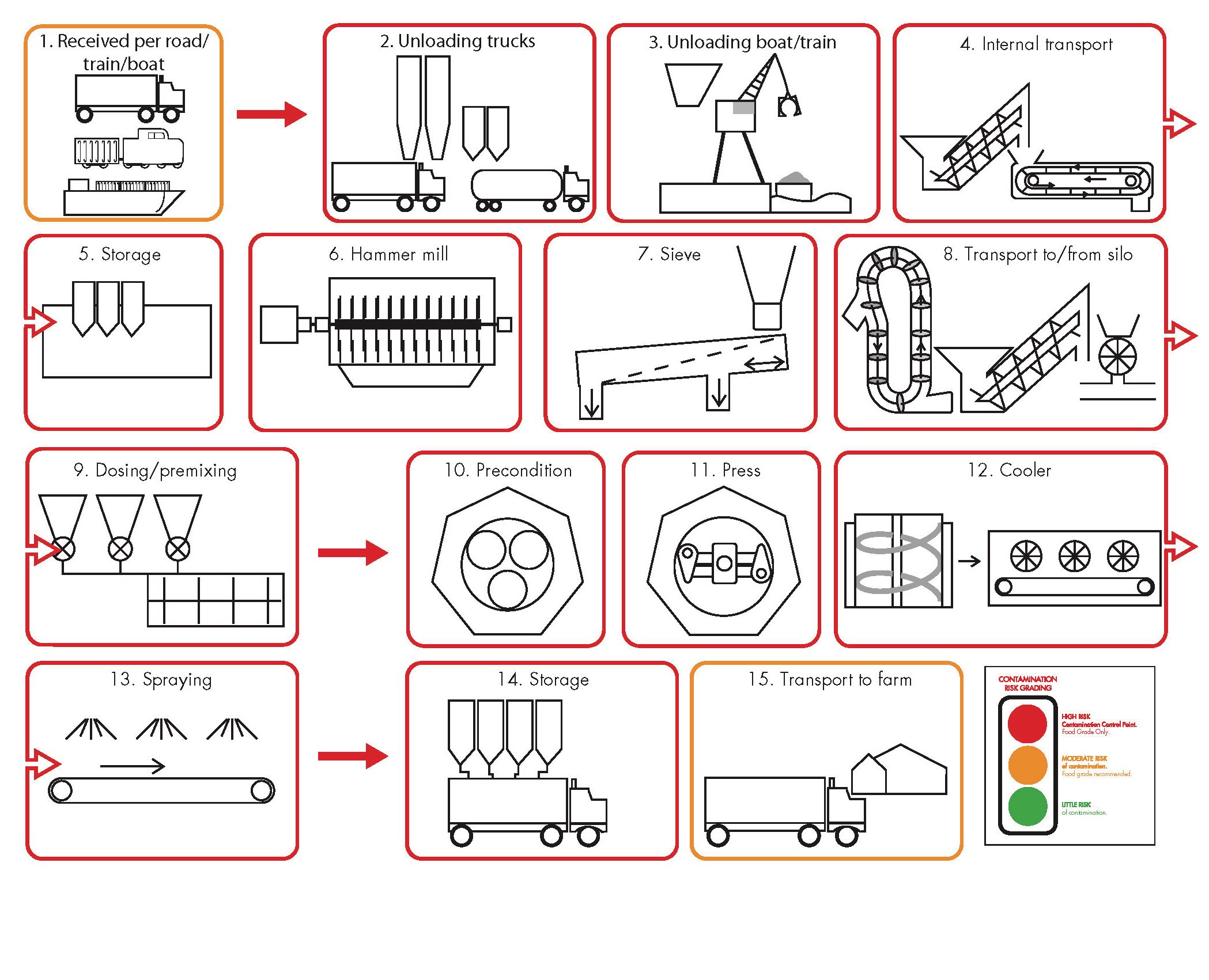
Steps in animal feed preparation and recommended lubricants.
1. Receival ingredient per boat / train / truck
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| .. Grain | - | - |
| .. Sugar byproducts | - | - |
| .. Fat/oil/fatty acids | - | - |
| .. Small functional ingredients | - | - |
2. Unloading (tanker), transport to tank
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| air compressor - blower | oil-free air | Cassida HF 100 or CR 100 |
| air compressor - piston | compressor oil | Cassida CR 100 |
| pump - gear box | gear oil | Cassida GL 220 or GL 460 (for worm gear) |
| stirrer - gear box | gear oil | Cassida GL 220 or GL 460 (for worm gear) |
3. Unloading (crane)
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| bucket | grease NLGI 2, water resistant | Cassida EPS 2 or HDS 2 |
4. Transport to silo
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| conveyor - roller bearings | filled for life | Cassida EPS 2 or HDS 2 |
5. Storage in silo
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| - | - | - |
6. Milling
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| hammermill - roller bearings | grease NLGI 2, water resistant | Cassida RLS 2 or HTS 2 (high temperature) |
7. Sieve
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| gear box | gear oil | Cassida GL 220 or GL 460 (for worm gear) |
| sliding blocks | grease NLGI 2, water resistant | FM grease HD2 |
8. Transport to silo
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| screw conveyor - gear box | gear oil | Cassida GL 220 or GL 460 (for worm gear) |
| bucket conveyor - gear box | gear oil | Cassida GL 220 or GL 460 (for worm gear) |
| rotary vavle - gear box | gear oil | Cassida GL 220 or GL 460 (for worm gear) |
9 Dosing and pre mixing
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| rotary valve - gear box | gear oil | Cassida GL 220 or GL 460 (for worm gear) |
10. Preconditioner
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| hydraulic | hydraulic oil | Cassida HF 68 |
| gear box | gear oil | Cassida GL 220 or GL 460 (for worm gear) |
| roller bearings | grease NLGI 2, water resistant | Cassida EPS 2 or FM HD2 |
11. Press
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| hydraulic | hydraulic oil | Cassida HF 68 |
| roller adjustment | grease NLGI 2, water resistant | Cassida EPS 2 or HDS 2 |
| gear box | gear oil | Cassida GL 220 or GL 460 (for worm gear) |
12. Cooler
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| gear box | gear oil | Cassida GL 220 or GL 460 (for worm gear) |
| roller bearings | grease NLGI 2, water resistant | Cassida EPS 2 or HDS 2 |
13. Spraying heat sensitive ingredients
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| gear box | gear oil | Cassida GL 220 or GL 460 (for worm gear) |
| roller bearings | grease NLGI 2, water resistant | Cassida EPS 2 or HDS 2 |
14. Storage in silo
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| - | - | - |
15. Transport to farm
| lubricate | application | food grade -H1 compliant option |
|---|---|---|
| air compressor - blower | oil-free air | Cassida HF 100 or CR 100 |
| air compressor - piston | compressor oil | Cassida CR 100 |
Switch to food grade lubricants
High-performance lubricants and greases play an important role in ensuring reliable and efficient operation of production machinery. For food manufacturers, the use of machinery and components such as mixers, pumps, sterilisers, can seamers, and conveyor belts are vital to their operations.
Lubricants and greases can present a serious threat to food safety if they come into contact with foodstuffs. The risk is best minimised through a number of measures, namely good engineering design, hygienic operations and the use of food grade lubricants. This last measure, the use of food grade lubricants, is becoming increasingly common. Companies make the switch away from traditional mineral-based products to ensure maximum food safety and to protect their brands. This has been fostered by more rigorous safety regulations, and as a result, food manufacturers tend to switch over to food grade lubricants completely.

Minimum risk
With exacting demands placed on modem day processing equipment, food producers are looking for continuous, 24/7 production. This combined with the specific lubricant needs of specialist equipment such as rotary cookers (sterilisers), can seamers and separators, means that high-performance food grade lubricants are vital to business success, ensuring maximum productiviry and minimum risk.
Over the last decade the work of the US Department of Agriculture and the Food & Drug Administration, and recently the governmental organisation NSFInternational (which has taken over food grade lubricant registration from the USDA), has been well documented and well received by the food industry.
The FDA produces a list of non-food components which are permitted in food grade lubricants. NSF verifies the formulations of these food grade lubricants and registers them as Hl. This is especially important in furthering the correct use of food grade lubricants across the industry.

Threat
EHEDG (European Hygienic Equipment Design Group) also produces industry guidelines which focus on the use of lubricants in food and beverage manufacturing. These guidelines describe the typical contamination points, which may be LCPs (Lubricant Control Points) in a Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point system (HACCP). EHEDG also provides many recommendations covering the production and use of food grade oils and greases.
Whilst improving engineering design at Critical Control Points (CCPs) can reduce the likelihood of contamination, it is not always possible to eliminate these risks. Therefore incidental contact of lubricants with food products is an ever-present threat. By regularly monitoring lubricant control points and using Hl food-grade lubricants, companies can effectively reduce the risk or contamination, without compromising food quality and protecting both the consumer and the brand."
Featured expert: Pieter Van de Schepop